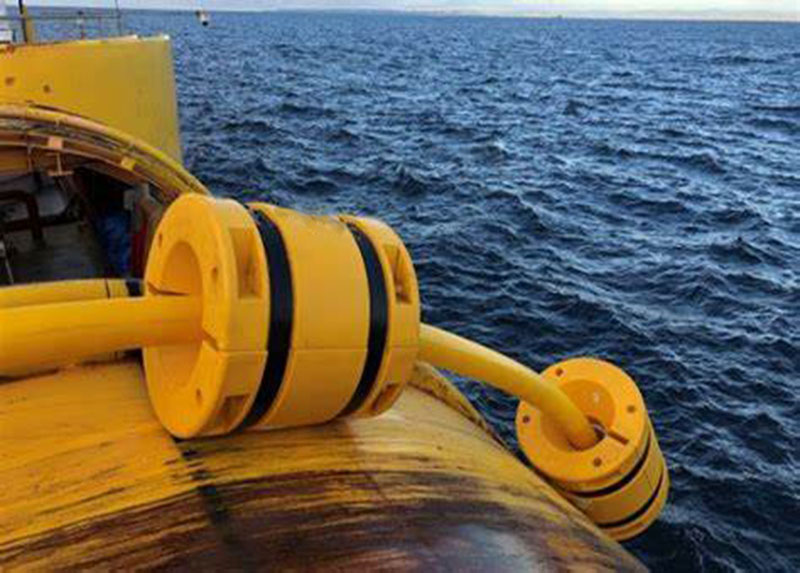
In offshore oil and gas development, flexible riser (flexible pipe) is a key equipment connecting the submarine wellhead and the offshore platform, and is widely used in deep-sea oil and gas development, offshore wind farms, and floating platform projects. Due to the complex marine environment, the riser is often subjected to dynamic loads from waves, ocean currents, and platform movement, and is prone to fatigue damage in the bending area (such as suspension points and touchdown points). As an important protection component, the polyurethane flexible riser bending stiffener (Bend Stiffener) can effectively disperse stress and inhibit excessive bending, thereby extending the service life of the riser. This article will focus on the role, design features, and installation precautions of the bending stiffener.

Functions of bending stiffeners
1. Prevent excessive bending and protect the riser structure
Flexible risers are prone to local bending due to waves or platform movement in dynamic marine environments, exceeding their minimum bending radius (MBR), resulting in damage to internal reinforcement layers (such as armored steel wire and pressure-resistant layer). The stiffeners provide progressive stiffness support and limit the bending curvature to ensure that the riser always deforms within a safe range.
2. Disperse dynamic loads and reduce fatigue risks
The tapered design of the stiffeners can smoothly transition bending stress and avoid stress concentration, thereby reducing the risk of fatigue crack initiation in the riser under alternating loads.
3. Resist external impact and wear
In the contact area between the riser and the platform (such as the I/J-type pipe suspension point), the stiffeners can buffer the friction between the riser and the structure and prevent wear or chemical corrosion of the sheath layer.
Design features
1. Material selection: high-performance polyurethane elastomer
Polyurethane (PU) is the mainstream material for stiffeners because of its advantages:
High elastic modulus (wide adjustable range, usually 50–500 MPa), adaptable to different stiffness requirements.
Resistant to seawater corrosion and UV aging, with a service life of more than 20 years.
Excellent fatigue resistance, not easy to crack under dynamic load.
2. Structural design: tapered, gradual stiffness
Geometry: Usually a tapered sleeve with a length of 1-5 meters, the small end diameter matches the riser, and the large end diameter gradually increases to provide a stiffness gradient.
Internal structure: Some reinforcement ribs have built-in metal skeletons (such as glass fiber or carbon fiber reinforcement layers) to further enhance bending resistance.
3. Key parameters
Minimum bending radius: 1.5-3 times the riser diameter to avoid plastic deformation of the riser reinforcement layer
Axial stiffness: progressive increase (top > bottom), smooth transition stress
Operating temperature: -30°C to +80°C, suitable for deep sea or polar environments
Installation precautions
1. Pre-installation inspection
Matching verification: Ensure that the inner diameter of the reinforcement rib matches the outer diameter of the riser (usually 0.5-1 mm interference) to avoid sliding or loosening.
Surface treatment: The contact surface of the riser should be clean and free of oil. If necessary, apply a special adhesive (such as polyurethane glue) to enhance the bonding force.
2. Installation process
Positioning mark: Determine the installation position of the reinforcement rib at the place where the risk of bending of the riser is the highest (such as below the suspension point).
Heating assembly (optional): Heat the polyurethane reinforcement rib to 60–80°C (softening temperature) to facilitate insertion into the riser.
Curing and fixing: Cool naturally or use a clamp to fix for 24 hours to ensure a close fit with the riser.
3. Common problems and countermeasures
Problem 1: Gaps appear between the reinforcement rib and the riser.
Countermeasure: Use a segmented design or add a filling layer (such as polyurethane foam).
Problem 2: Polyurethane ages and hardens after long-term use.
Countermeasure: Choose a hydrolysis-resistant polyurethane (such as polyether TPU) and regularly test hardness changes.
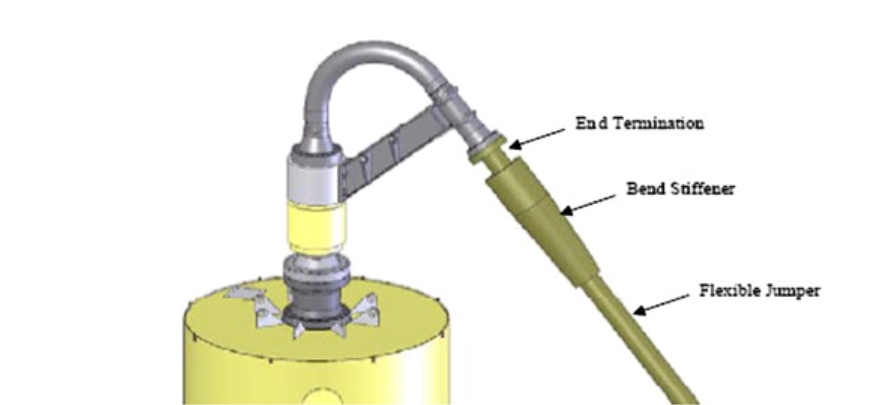
Polyurethane flexible riser bending stiffener the core component to ensure the safe operation of marine risers. Its gradual stiffness design, corrosion-resistant materials, and precise installation work together to significantly improve the reliability of risers in dynamic environments. In the future, with the development of deep-sea oil and gas development and offshore wind power, lightweight and intelligent reinforcement (such as embedded strain sensors) will become the direction of technology upgrades.




